Technical Benefits
Field Test 4G Mobile Signal Strength
Want to know if Outdoor 4G Router works for you? Do a simple field test on your mobile phone by use your mobile phone to check the signal quality outside your house.
Step 1
Go outdoor your home or office with your mobile phone.
Step 2
Disable Wi-Fi connection on your mobile phone, then you to see what network you’re connecting to (2G, 3G, 4G, LTE, etc.).
Step 3
Take note of signal bars and the symbol in the status bar of your mobile phone and compare with below chart.
| Symbol | Mobile Networks | Voice Call | Internet Speed | Email & Notification | Video |
| G | GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) |
Yes | 50Kbits/s | Yes | No |
| E | EDGE (Enhanced Data GSM Evolution) |
Yes | 100Kbits/s | Yes | No |
| 3G | Third Generation also known as UMTS / WCDMA / CDMA2000 |
Yes | 2Mbits/s | Yes | Yes |
| H/H+ | HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access) |
Yes | 10-100Mbits/s | Yes | Yes |
| 4G (LTE) | Fourth generation or Long term evolution also known as LTE or WiMax |
Yes | 100Mbits/s+ | Yes | Yes |
| No Symbol | If signal bars get more than 1 bar you can use voice call |
N/A | No | No | No |
In your mobile phone, you can read signal bars followed by carrier name and network symbol which usually maxes 5~8 bars. To measure mobile phone’s signal reception in exact decibels instead of bars or dots, you can follow step 4 to enter Field Test Mode in mobile phones.
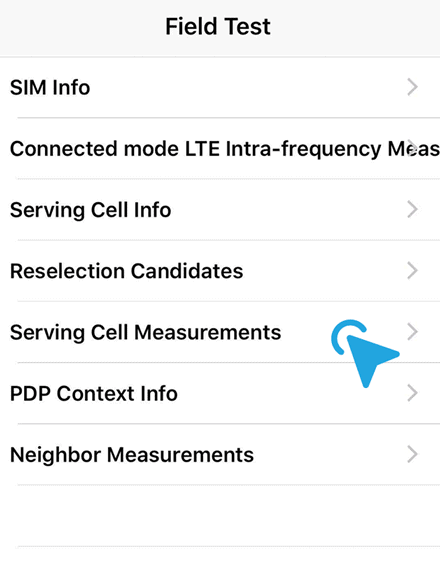
Step 4 – in iPhone iOS 12
i. Go into the Phone app and switch to the Keypad. Dial *3001#12345#* and press Call button.
It will launch the Field Test Mode app on your mobile phone.
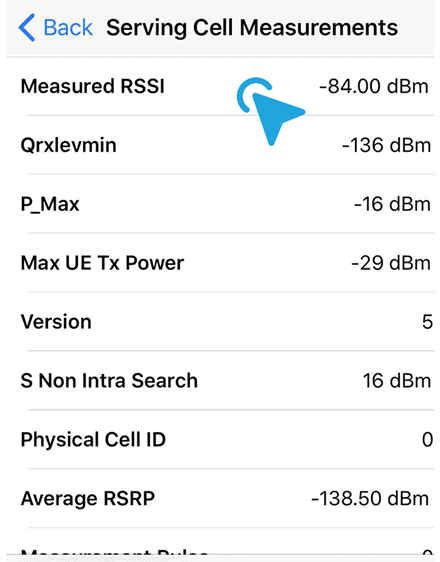
ii. In the latest iOS 12, tap on Serving Cell Measurements.
iii. Look for Measured RSSI with numerical measurement of the iPhone 4G LTE cellular signal strength in dBm.
RSSI stands for Received Signal Strength Indicator
RSRP stands for Reference Signal Received Power
RSRQ stands for Reference Signal Received Quality
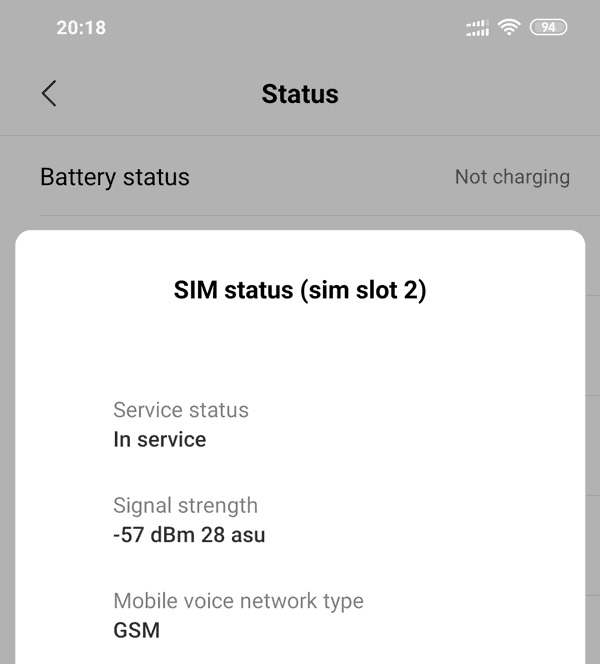
Step 4 – in Android Smartphone
Go to Settings > About Phone > Status > SIM Status and numerical signal strength will be available on either network or status which depends on the model of phone.
You can also use apps to show signal strength in decibels in Android phones.
Remarks:
1) The numerical value of 2G / 3G / 4G H+ networks is RSSI standard which is Received Signal Strength Indicator. LTE network is RSRP standard which is Reference Signal Receive Power. Hence, you need to turn off LTE on your mobile phone before entering Field Test Mode.
2) Decibel signal strengths will be negative 2~3 digits. Unit of measurement is dB. If your phone show a number such as 98, the actual signal strength is -98dB. The closer the number is to zero, the better the reception, so -90dB is a stronger signal than -100dB.
Signal bars VS decibel signal strength
| Signal Bars | iPhone Mobile | Nokia Phone |
| 5 | > -85 dBm | > -91 dBm |
| 4 | -85 ~ -90 dBm | -91 ~ -101 dBm |
| 3 | -90 ~ -95 dBm | -101 ~ -103 dBm |
| 2 | -95 ~ -100 dBm | -103 ~ -107 dBm |
| 1 | -100 ~ -105 dBm | -107 ~ -113 dBm |
| 0 | < -105 dBm | < -113 dBm |
4G LTE Bands and Frequencies
4G mobile phone networks has two different standards FDD LTE and TDD LTE. Both of them are used to maximize the available bandwidth.
FDD LTE uses a paired spectrum with different frequencies to transmitting (uplink) and receiving (downlink) signals simultaneously. TDD LTE uses unpaired spectrum because the working frequency for transmitting (uplink) and receiving (downlink) is exactly same.
| FDD-LTE Band | Uplink | Downlink | Band Width | Duplex Spacing | Guard Band |
| B1 | 1920 – 1980 MHz | 2110 – 2170 MHz | 60 MHz | 190 MHz | 130 MHz |
| B2 | 1850 – 1910 MHz | 1930 – 1990 MHz | 60 MHz | 80 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B3 | 1710 – 1785 MHz | 1805 – 1880 MHz | 75 MHz | 95 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B4 | 1710 – 1755 MHz | 2110 – 2155 MHz | 45 MHz | 400 MHz | 355 MHz |
| B5 | 824 – 849 MHz | 869 – 894 MHz | 25 MHz | 45 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B6 | 830 – 840 MHz | 875 – 885 MHz | 10 MHz | 35 MHz | 25 MHz |
| B7 | 2500 – 2570 MHz | 2620 – 2690 MHz | 70 MHz | 120 MHz | 50 MHz |
| B8 | 880 – 915 MHz | 925 – 960 MHz | 35 MHz | 45 MHz | 10 MHz |
| B9 | 1749.9 – 1784.9 MHz | 1844.9 – 1879.9 MHz | 35 MHz | 95 MHz | 60 MHz |
| B10 | 1710 – 1770 MHz | 2110 – 2170 MHz | 60 MHz | 400 MHz | 340 MHz |
| B11 | 1427.9 – 1452.9 MHz | 1475.9 – 1500.9 MHz | 20 MHz | 48 MHz | 28 MHz |
| B12 | 698 – 716 MHz | 728 – 746 MHz | 18 MHz | 30 MHz | 12 MHz |
| B13 | 777 – 787 MHz | 746 – 756 MHz | 10 MHz | – 31 MHz | 41 MHz |
| B14 | 788 – 798 MHz | 758 – 768 MHz | 10 MHz | – 30 MHz | 40 MHz |
| B15 | 1900 – 1920 MHz | 2600 – 2620 MHz | 20 MHz | 700 MHz | 680 MHz |
| B16 | 2010 – 2025 MHz | 2585 – 2600 MHz | 15 MHz | 575 MHz | 560 MHz |
| B17 | 704 – 716 MHz | 734 – 746 MHz | 12 MHz | 30 MHz | 18 MHz |
| B18 | 815 – 830 MHz | 860 – 875 MHz | 15 MHz | 45 MHz | 30 MHz |
| B19 | 830 – 845 MHz | 875 – 890 MHz | 15 MHz | 45 MHz | 30 MHz |
| B20 | 832 – 862 MHz | 791 – 821 MHz | 30 MHz | – 41 MHz | 71 MHz |
| B21 | 1447.9 – 1462.9 MHz | 1495.9 – 1510.9 MHz | 15 MHz | 48 MHz | 33 MHz |
| B22 | 3410 – 3500 MHz | 3510 – 3600 MHz | 90 MHz | 100 MHz | 10 MHz |
| B23 | 2000 – 2020 MHz | 2180 – 2200 MHz | 20 MHz | 180 MHz | 160 MHz |
| B24 | 1625.5 – 1660.5 MHz | 1525 – 1559 MHz | 34 MHz | – 101.5 MHz | 135.5 MHz |
| B25 | 1850 – 1915 MHz | 1930 – 1995 MHz | 65 MHz | 80 MHz | 15 MHz |
| B26 | 814 – 849 MHz | 859 – 894 MHz | 35 MHz | 45 MHz | 10 MHz |
| B27 | 807 – 824 MHz | 852 – 869 MHz | 17 MHz | 45 MHz | 28 MHz |
| B28 | 703 – 748 MHz | 758 – 803 MHz | 45 MHz | 55 MHz | 10 MHz |
| B29 | N/A | 717 – 728 MHz | 11 MHz | N/A | N/A |
| B30 | 2305 – 2315 MHz | 2350 – 2360 MHz | 10 MHz | 45 MHz | 35 MHz |
| B31 | 452.5 – 457.5 MHz | 462.5 – 467.5 MHz | 5 MHz | 10 MHz | 5 MHz |
| TDD-LTE Band | Frequency | Band Width |
| B33 | 1900 – 1920 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B34 | 2010 – 2025 MHz | 15 MHz |
| B35 | 1850 – 1910 MHz | 60 MHz |
| B36 | 1930 – 1990 MHz | 60 MHz |
| B37 | 1910 – 1930 MHz | 20 MHz |
| B38 | 2570 – 2620 MHz | 50 MHz |
| B39 | 1880 – 1920 MHz | 40 MHz |
| B40 | 2300 – 2400 MHz | 100 MHz |
| B41 | 2496 – 2690 MHz | 194 MHz |
| B42 | 3400 – 3600 MHz | 200 MHz |
| B43 | 3600 – 3800 MHz | 200 MHz |
| B44 | 703 – 803 MHz | 100 MHz |